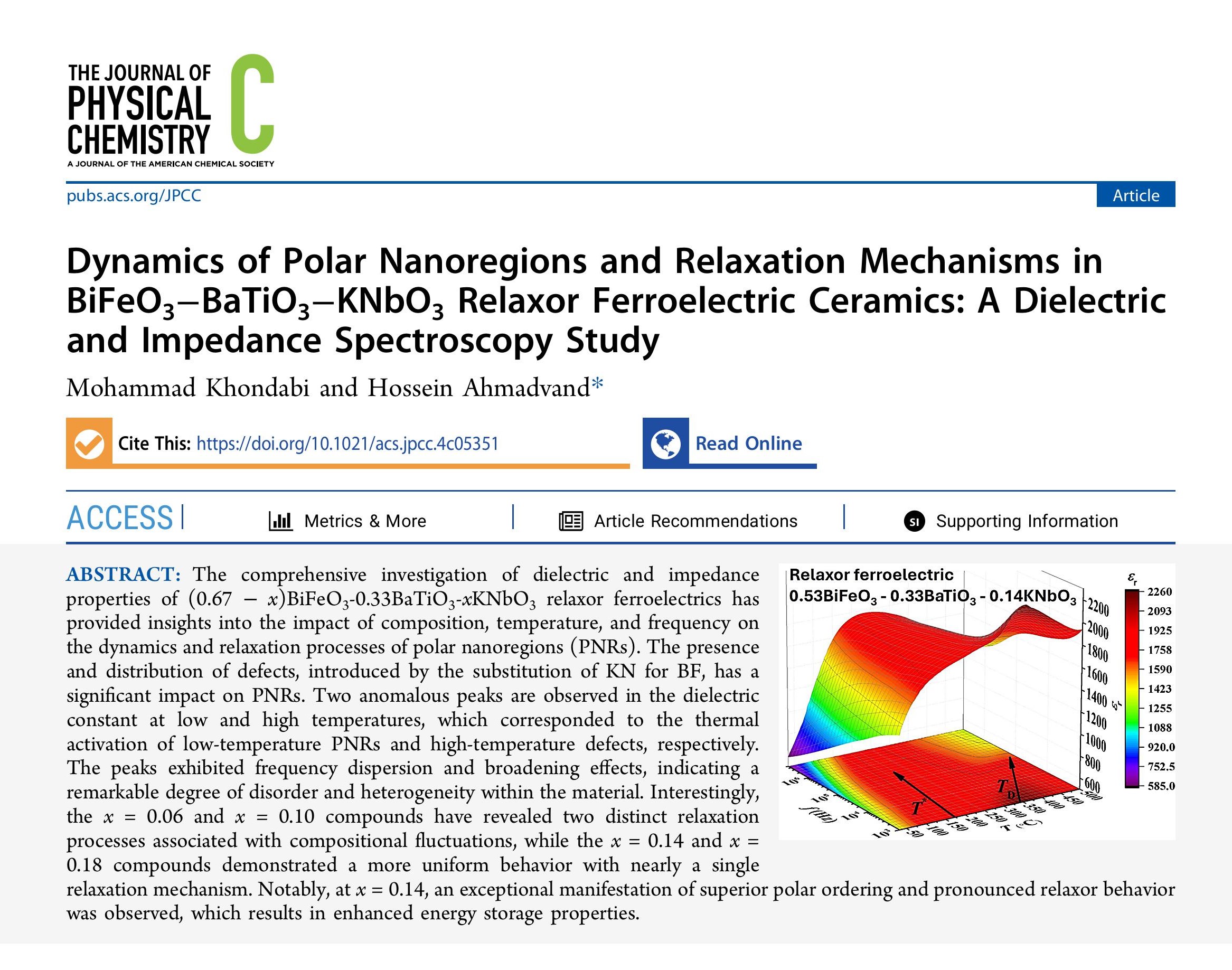
ABSTRACT: The comprehensive investigation of dielectric and impedance properties of (0.67 − x)BiFeO3-0.33BaTiO3-xKNbO3 relaxor ferroelectrics has provided insights into the impact of composition, temperature, and frequency on the dynamics and relaxation processes of polar nanoregions (PNRs). The presence and distribution of defects, introduced by the substitution of KN for BF, has a significant impact on PNRs. Two anomalous peaks are observed in the dielectric constant at low and high temperatures, which corresponded to the thermal activation of low-temperature PNRs and high-temperature defects, respectively. The peaks exhibited frequency dispersion and broadening effects, indicating a remarkable degree of disorder and heterogeneity within the material. Interestingly, the x = 0.06 and x = 0.10 compounds have revealed two distinct relaxation processes associated with compositional fluctuations, while the x = 0.14 and x = 0.18 compounds demonstrated a more uniform behavior with nearly a single relaxation mechanism. Notably, at x = 0.14, an exceptional manifestation of superior polar ordering and pronounced relaxor behavior was observed, which results in enhanced energy storage properties.